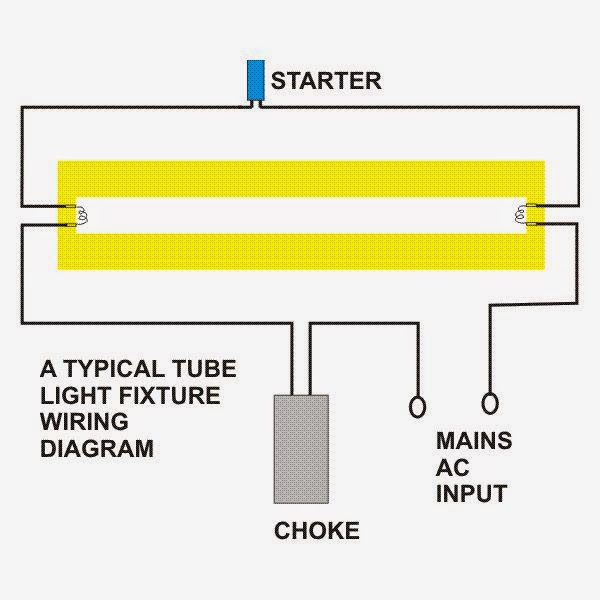
Faults in Electrical Lighting system and Most Severe Fault in lights
We often observe day to electrical faults in our appliances such as 1.Tube rod get faulty 2. Lights not working these are all happens due to Aging of equipment's Below are the faults which are not in control:- 1. High voltage from source 2. Low voltage from source these types of abnormalities usually effect electronic equipment's such as TV, fridge, Microwave etc. So to avoid faults in these equipment's usually Stabilizers are installed for them. So that any abnormality in source voltage could not effect our load end. But severe fault occurred when neutral get breaker from transformer in that case in that case Neutral becomes a floating neutral and phase starts coming in Neutral. Which causes burning of every equipment and even may cause fire if lights not switched off in line. Now Question arises How voltage starts coming in Neutral? Answer for the same is that During neutral break if Transformer load is balanced then ...