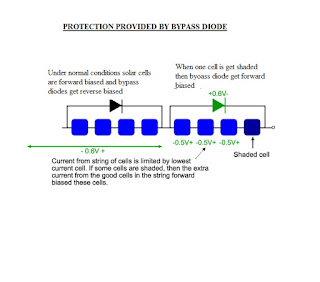
Voltage drop reduction methods; Voltage drop an evil in electrical systems

Voltage Drop in Electrical Systems: Causes, Effects, and Solutions Voltage drop is one of the most common problems electrical engineers deal with. It reduces the effective utilization of generated voltage and increases power losses in transmission and distribution systems. While some voltage drop is inevitable, minimizing it is essential for efficiency, safety, and compliance with electrical standards. Understanding Voltage Drop The fundamental relation is: V = I × R V = I \times R Where: V = Voltage drop across conductor I = Current through conductor R = Resistance of conductor Now, conductor resistance is: R = ρ × L A R = \rho \times \frac{L}{A} Where: ρ (rho) = Resistivity of conductor material L = Length of conductor A = Cross-sectional area of conductor Combining these, V = I × ρ × L A V = I \times \rho \times \frac{L}{A} So, voltage drop is directly proportional to current (I) and length (L) , and inversely proportional to cross-section...