Variable Refrigerant flow Air conditioning; VRV System
Variable
Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems
Variable refrigerant flow type Air conditioners also known as
Variable Flow Volume i.e. VRV, Where variable refrigerant means the ability of
the system to control the amount of refrigerant flowing to multiple evaporators
i.e. indoor units. Actually VRV consists of multiple Indoor units and all are
connected to one single outdoor unit.
VRV also provide the individual settings of all Indoor units and
it can handle both heating and cooling in different zones simultaneously. VRV
were originally manufactured by Diakin, Japan. These are more widely used for
Industrial applications where ducting isn’t possible.
There is one problem that Design
of VRF systems is more complicated and requires additional work compared to
designing a conventional direct expansion (DX) system.
Let’s how VRV is different from other Air
conditioning systems:-
Split Air-conditioning
Split type air conditioning you have often seen which consists of
one indoor unit along with one oudoor unit i.e. every indoor unit and outdoor
unit will constitute a single split AC.
Few advantages and
Disadvantages of Spilt AC’s
Advantages:-
1.
These AC’s have low initial cost
2. Ease
of installation
3. No
ducting required
4. Each
system have own control.
Disadvantages
• Distance between indoor and outdoor unit should not be greater
than 100- 150 ft otherwise the performance will suffer.
• Limited air throw.
Multi-Split Systems
This system operates similar to split type air- conditioning
system however difference is that in this case there are ‘multiple’ evaporator
units connected to one external condensing unit. These type of systems were designed mainly for
small to medium commercial applications. These are basically used where ducting
isn’t possible.
Each indoor unit has its own set of refrigerant pipe work
connecting it to the outdoor unit.
Advantages of Multi-splits
•
No need of duct work installation.
·
System efficiency improves then individual Split unit
•
Multi-splits are suitable for single thermal zone applications i.e.
either for cooling mode or heat mode.
Drawbacks
• Main Drawback is that Individual system control not possible.
• In this systems whole system will turn OFF or ON completely in
response to a single thermostat. These systems are therefore not suitable for
areas/rooms with variable heat gain/loss characteristics.
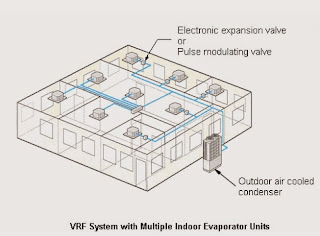
Variable Refrigerant Flow Or VRV
These type of air conditioners are similar to the multi-split
systems which connect one outdoor section to several evaporators main
difference is that in multi-split systems there is only one controller which
turns OFF or ON completely in response to one master controller. But in VRV
systems can adjust the flow of refrigerant to each indoor evaporator.
The control of refrigerant is achieved by continually varying the
flow of refrigerant through a pulse modulating valve. Opening of Pulse
modulating valve is done by the microprocessor receiving information from the
thermistor sensors in each indoor unit.
The indoor units are linked by a control wire to the outdoor unit
which responds to the demand from the indoor units by varying its compressor
speed to match the total cooling and/or heating requirements.
VRV systems are efficient than air conditioning options and usually
save 10- 20% electricity. But they have some high initial cost. Today in modern
technology when there is inverter
controlled technology has arrived which will leads to as many as 48 or more indoor
units to operate from one outdoor unit .
With VRV refrigerant piping runs of more than 200 ft are possible,
and outdoor units are available in sizes up to 240,000 Btuh.





Nice Post! Thanks for sharing valuable information about VRF Air Conditioning System
ReplyDelete